Forest Flows was a five-year research programme that aimed to answer questions about trees, water and forests' role in the landscape. Scion led the MBIE-supported programme, working in collaboration with various iwi, national and international universities, and institutes.
Understanding how water flows through the land, including planted forests is essential to make the best use of land and water while maintaining environmental health. New research is needed to replace outdated models and understand the complex processes of how water is distributed, used and circulated in forested catchments.
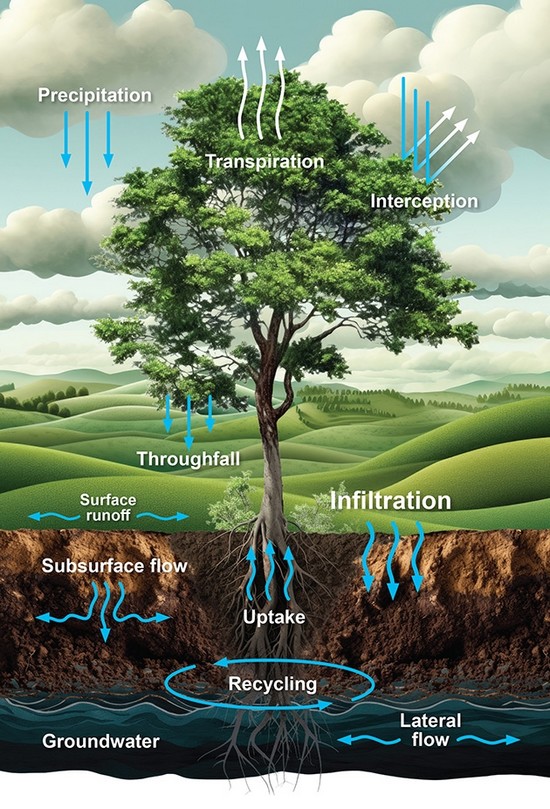
Why Forest Flows?
- Increasing concern with water availability and quality
- Concern about impact of large-scale forest plantings
- increasing questions on how much water radiata pine and other tree species use, and downstream impacts of water supply
- Little research in forest hydrology over the last 40 years
- Outdated forest hydrology models
Innovative Technology
Forest Flows successfully combined cutting edge remote sensing techniques with terrestrial based measurements, integrating data and enabling at different scales, from tree, to stand, to catchment and forest, as a digital twin model applicable to planted forest catchments across New Zealand.
These extrapolations will be made possible through the various novel technologies used in the programme.
Main findings
Through direct measurements, we were able to quantify tree water use, catchment water storage and release.
The main findings are summarised in a series of infosheets:

| Forest Hydrology, an overview of how water moves and is stored in forest environments. |
 | Forest water release, water movement within and out of the forest. |
 | Predicting stream flow from forested catchments, a new model developed in Forest Flows predicts streamflow and water balance |
 | Stream nitrate in planted forests, how do forests impact water quality, measured by stream nitrate concentration. |
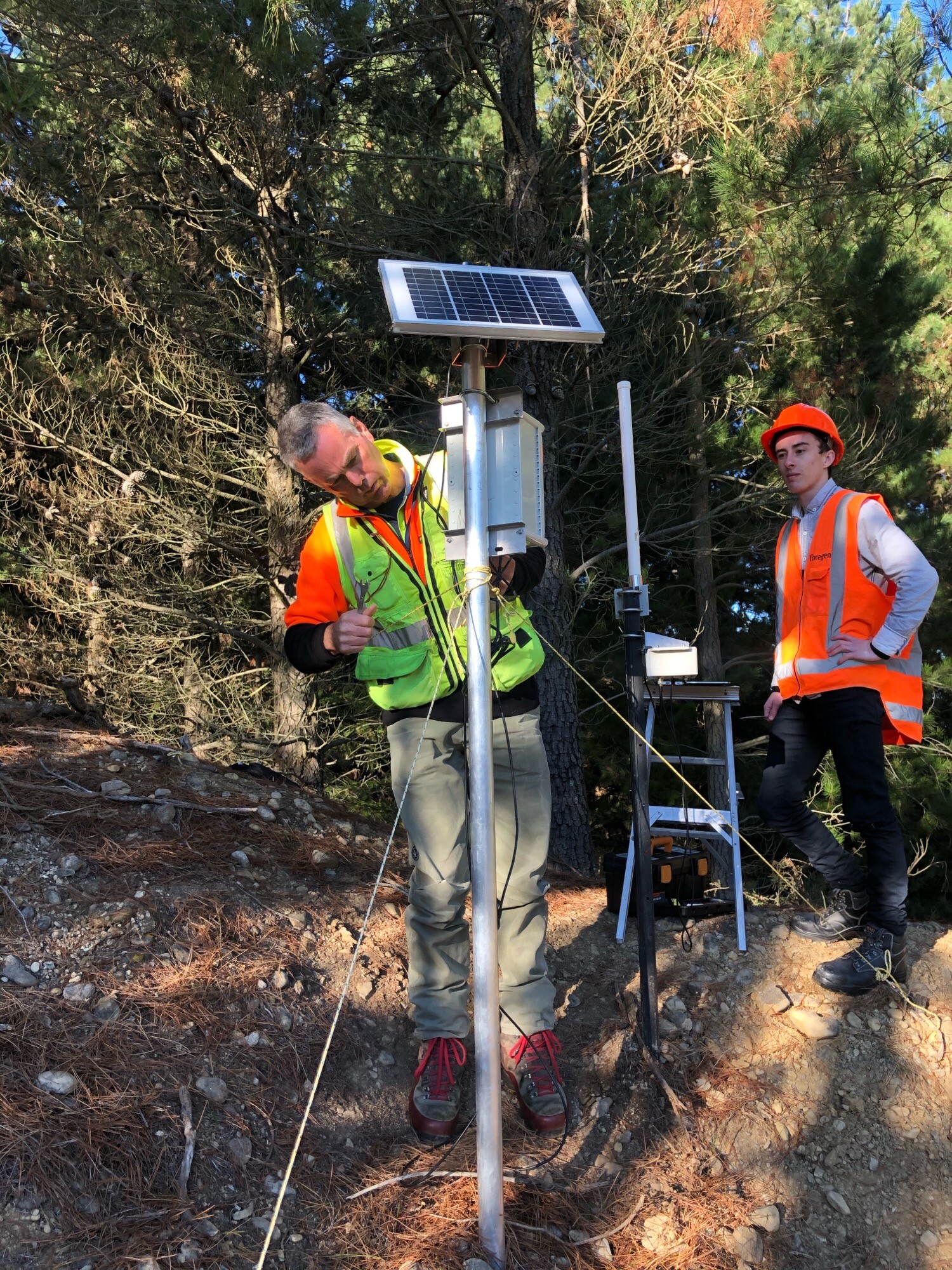

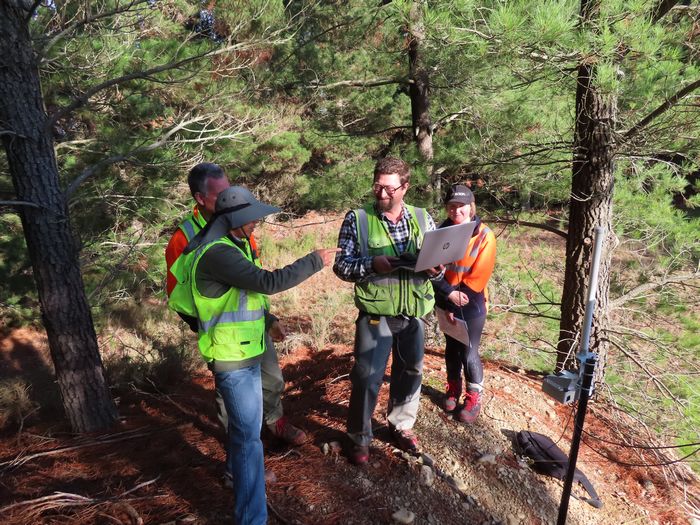
Forest Flows Measurements
We used a range of traditional and new approaches to take direct measurements to answer the questions: Where is the water? Where is it going? And who gets to use it?
- Nine research sites throughout New Zealand, including five primary sites across a rainfall gradient (800-3000 mm/yr) with different geology, soils, and climate
- Integrated remote sensing and terrestrial measurements above and below ground
- 1717 terrestrial sensors, 360,000 observations a day, 130 million observations a year
- Scion’s sensors managed by wireless IoT meshed FlowLab Datalogger network
- FlowLab Network Data streamed, cleaned and stored by the Kafka Big Data Pipeline
- Near real-time data provided the “pulse” of the forest
Science outputs
There have been 13 scientific articles published to date and more are in progress.

Community and Māori engagement
Forest Flows engaged with three local communities near to our research sites: Far North, Tararua District, and Masterton District. An objective of the programme was to have regular, in person engagement with our local communities so we could understand the views of our different stakeholders.
- Read more about our community and iwi engagement.

Related links
- Extreme rainfall - Forest Flows (NZ Tree Grower)
- When the rain pours, where does the water flow? (Scion Connections)
- Maimai conference and Forest Flows (News item)
- NZ’s new plan for clean water (NZ Herald)
- Researchers seek to impact New Zealand water quality by understanding forest-water interactions (Virginia Technology)
- Solving the mysteries of forest hydrology (Scion Connections)
Contact
Dean Meason, Scientist, Plant Morphology and Physiology

